What is Quantum Computing?
If you think Quantum Mechanics sounds challenging, then you are not alone. All of our intuitions are based on day-to-day experiences and so better at understanding the behaviour of balls and bananas than understanding the behaviour of atoms and electrons. Though quantum objects seem to be random and chaotic at first, they just follow a set of rules, which are different from our regular physics i.e Newtonian Physics or Classical physics.
Once we know these set of rules, we can build new and powerful technologies. Quantum Computing is one of them, revolutionary technology.
So, What is Quantum Computing?
By the definition, Quantum Computing is a computational process that leverages upon specific quantum properties like Quantum Superposition and Quantum Entanglement to perform computation.
Gone over head ? No worries we will get into it in a simpler way!
To understand the Quantum Computing lets first understand how a classical Computing works.
What do think, the following image shows ?
You would have pronounced this as a letter “A”.
Correct !
Now, Can you guess how a computer(processor) would think about this?
This series of 0’s and 1’s is called a Binary Number. This is how a letter “A” is stored and processed in a computer.
Every time we play a song or open an image or do any type of computation, at the backend these series of 0’s and 1’s are processed.
Exciting!!! Right?
A single 0 or 1 (states of a bit) is called a bit.
In classical Computing a bit can have either of these two values.
i.e bit = 1 or bit = 0.
But a bit cannot be in both of these states.
For example,
Let us toss a coin,
What will be the output of when the coin falls on the ground. It will have either of the two values “Heads” or “Tails”.
Can it be both “Heads” and “Tails” at the same time ? Think on it ?
Until then we will see whats inside a Quantum Computer,
As in Classical computer, Quantum Computer also has quantum bits called as “Qubits”.
A quantum bit posses two states 0 and 1 similar to the classical computer. All the computing is done on series of these two states.
So What makes a Quantum Computer Different? It is the quantum properties that a Qubit possesses.
Lets learn these properties in a Nutshell,
The first property of Qubit is Quantum Superposition,
Superposition is nothing but the linear combination of two or more states.
Lets consider the example of coin, but this time we will spin the coin instead of tossing it,
Can you guess the output while the coin is spinning ?
Obviously we cannot determine the output. But we can determine the probability of the output. The output can be “Heads” or “Tails” when the coin stops spinning.
Hence while spinning, the output of spinning coin is a linear combinations of two outputs Heads and Tails.
Similarly, a Qubit is in a linear combination of two states 0 and 1 i.e a Qubit is in superposition of two states. Which means at the time of computing two states are available at the same time for computing.
A number of states can be calculated by,
2^n = Number of states in Superposition.
If you have 2 qubits, 4 states are in superposition.
For 3 qubits, 8 states are in superposition.
For 4 qubits, 16 states are in superposition.
For 5 qubits, 32 states are in superposition.
As we increase the number of qubits the states in superposition increase exponentially. This makes the Quantum Computer to compute large data in much less time than classical computer.
Imagine how many states are there in a 5000 qubit computer or Quantum Computer with millions of Qubits!!!
Can you calculate??
As if Quantum Superposition were not odd enough, Quantum Mechanics describes a specific kind of superposition, called as Entanglement (EPR paradox) in which one system is corelated with the state of other system. In other words, the states of the two systems are not separable.
Consider the example of spinning coins, but this time lets consider two coins(C1 and C2) spinning, If these two coins are entangled then there output will be corelated.
Which means that, if C1 turns out to be heads than C2 will be tails and vice versa.
This shows that if we take two particles that are entangled with each other then the effect on one particle automatically triggers corelated state of the other particle- even if these two are at great distance.
Entanglement occurs only when two states are in superposition that are not separable.
All this was ok but why should we adapt Quantum Computing, instead of on going Classical Computing,
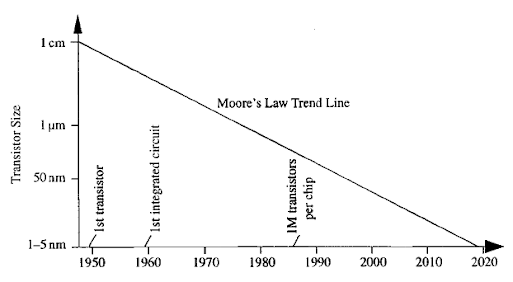
In classical Computers according to Moore's law the size of transistors is reduced day by day, as the transistors are becoming smaller and smaller they posses quantum properties like tunneling. Instead of following a classical path electrons gets tunneled to unwanted place. This is NOISE for classical computing. Due to which its hard to reduce the size of transistor and increase the computation power.
On the other hand Quantum Computers use Quantum Properties to perform Computation. And makes the Computation really really fast.
In this blog we have seen what is Quantum Computing. And two major Quantum properties that are used by Quantum Computers to perform Quantum Computation. In next blog we will learn about history of Quantum Computing and Applications of Quantum Computing.
So, Stay Tuned…. There’s lot to come.
HAPPY LEARNING !!!
Follow me on Instagram for exciting posts on Quantum Computing and Quantum Physics.
Do subscribe my blog. And do Share and Comment.








Awesome!
ReplyDeleteGood.
ReplyDeleteSo easy to understand
ReplyDeleteThank You!!
DeleteGreat job :)
ReplyDeleteVery good. You made it easy to understand.
ReplyDeleteThank you !!
DeleteLooks Good thank you for sharing :)
ReplyDelete